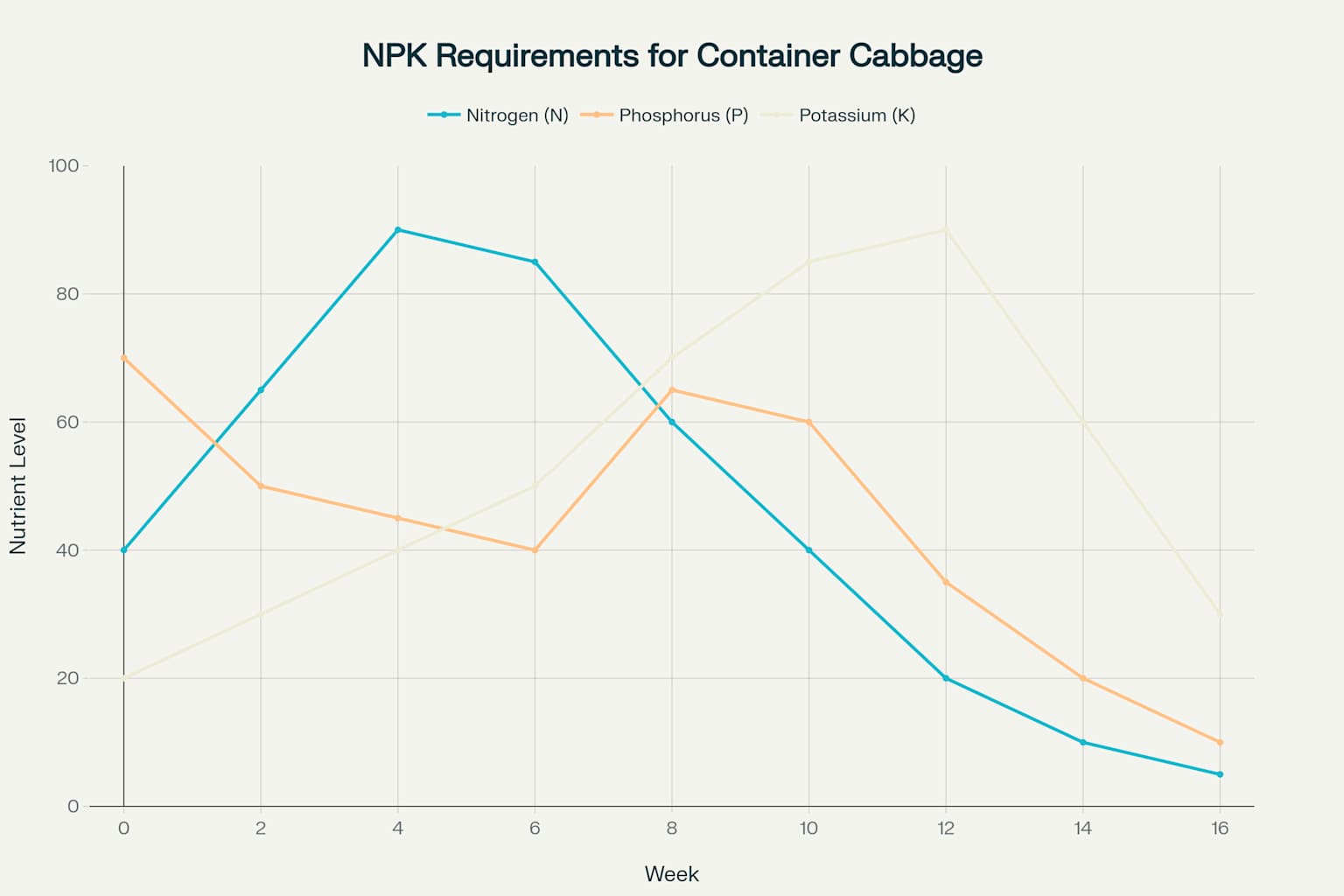
Nitrogen (N)
Total Season Need:
120-160 kg/ha equivalent
Peak Demand:
Weeks 2-6
Container Application:
Higher frequency, lower amounts
Signs of Deficiency:
Yellowing older leaves, stunted growth
Signs of Excess:
Excessive leaf growth, delayed heading, loose heads
Phosphorus (P)
Total Season Need:
50-100 kg/ha equivalent
Peak Demand:
Transplant and head formation
Container Application:
Essential at planting and week 8-10
Signs of Deficiency:
Purple leaf tinge, poor root development
Signs of Excess:
Reduced micronutrient uptake
Potassium (K)
Total Season Need:
180-200 kg/ha equivalent
Peak Demand:
Head formation and maturation
Container Application:
Increase during weeks 8-12
Signs of Deficiency:
Marginal leaf necrosis, poor head quality
Signs of Excess:
Reduced calcium and magnesium uptake